Beyond Telecoms ...
Telecom operators can no longer compete on connectivity alone. The future belongs to those who embrace a “beyond telco” vision—shifting from selling bandwidth to orchestrating value across ecosystems. Two domains are driving this transformation.
First, sustainability: operators must lead the way in energy efficiency, green IT, and next-generation datacenters, responding to mounting regulatory pressure and rising energy costs while meeting customer expectations for low-carbon services.
Second,smart cities: as urban environments evolve, telcos are uniquely positioned to integrate IoT, AI, cloud, and data platforms to enable smarter mobility, energy management, and citizen-centric services. Success requires moving up the value chain, becoming digital transformation partners that design and power the infrastructures of tomorrow—creating business impact, environmental value, and societal progress
Telecoms must transform from being part of the problem to becoming a catalyst of global decarbonization
The Global Picture: From Niche to Major Contributor
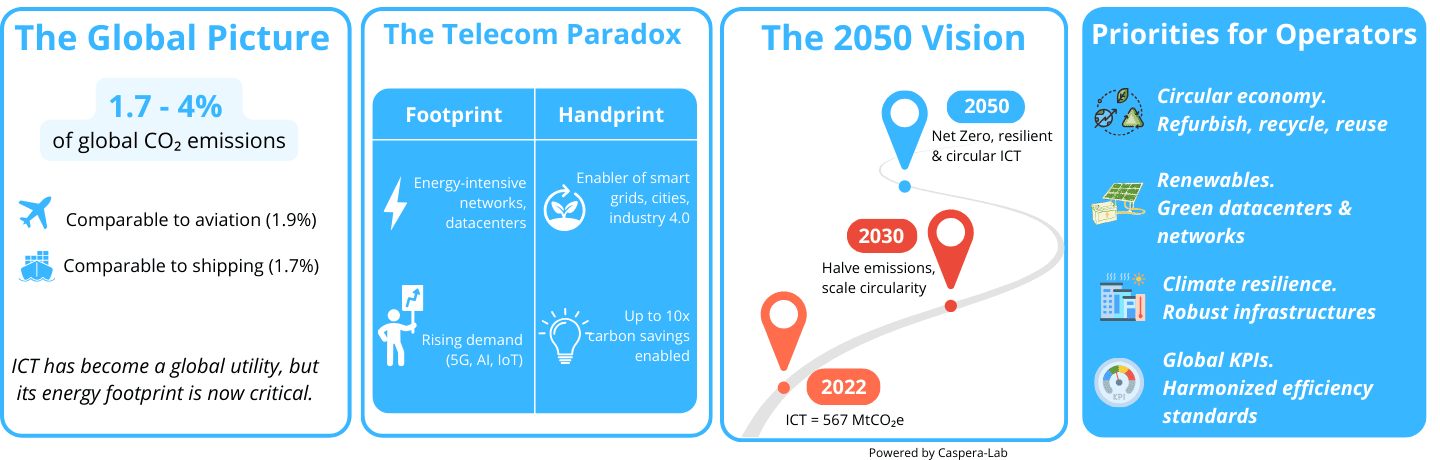
The information and communication technology (ICT) sector has evolved from a nascent industry into a pervasive global utility, now connecting two-thirds of the world's population. This rapid digitalization, however, carries a significant environmental footprint, primarily driven by increasing energy demands and associated greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Estimates of the sector's share of global carbon emissions vary widely across the literature, ranging from 1.5% to 4%. A recent report from the World Bank and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) places this figure at a minimum of 1.7% of global emissions as of 2022, representing 567 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent (tCO_2e). This places the ICT sector's environmental impact in a comparable class to the global aviation and shipping industries, which are responsible for 1.9% and 1.7% of global emissions, respectively.
The broad range in emission estimates is not an indication of a lack of rigorous analysis, but rather a symptom of the inherent complexity and a notable absence of standardized global metrics for measuring the sector's true environmental impact. The ICT ecosystem is vast and fragmented, encompassing everything from network infrastructure and data centers to a multitude of consumer devices. This lack of a unified measurement framework creates a data gap that can obscure the full scale of the industry's environmental responsibilities. In response, global organizations like the GSMA and ITU are actively working to address this issue by developing a common set of indicators and key performance indicators (KPIs) to better measure and compare energy efficiency across different networks and regions. These efforts are designed to provide a consistent view that accounts for factors beyond an operator's control, such as geography, climate, and spectrum holdings.
Despite its substantial footprint, the ICT sector also serves as a critical enabler of decarbonization for other industries, a concept often referred to as the industry's "handprint". Mobile and digital technologies, such as smart cities, smart grids, and smart manufacturing, are estimated to enable carbon reductions that are up to 10 times larger than the mobile industry's own carbon footprint. This dual role positions the sector as both a source of environmental challenge and a vital catalyst for the broader global green transition. The ongoing development of technologies such as AI and IoT is poised to further enhance these enabling capabilities, even as they contribute to the sector's own energy consumption.
The 2050 Vision: Goals and Milestones
The commitment to Net Zero by 2050, as set forth by the GSMA and embraced by a third of the industry, is more than a distant, aspirational target; it is a foundational framework that is driving urgent, near-term action. The goal aligns with the global scientific consensus on limiting temperature rise to 1.5°C, providing a clear and non-negotiable directive for the entire sector. The path to 2050 is not linear and requires a two-pronged approach: the rapid decarbonization of the sector itself, with a focus on substantial cuts needed by 2030, and the strategic use of ICT to help other industries decarbonize.
Achieving this vision necessitates a fundamental shift in business models, moving away from a linear, "take, make, and dispose" economy to a fully circular one where products and materials are continuously reused and repurposed. This requires a concerted effort to accelerate the implementation of circularity programs, from eco-design and refurbishment to end-of-life recycling and waste management. The 2050 target also includes an imperative for climate resilience, requiring operators to build robust networks that can withstand the increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events. The vision for 2050 is therefore a complete transformation of the industry, embedding sustainability into every aspect of its operations, from network design and deployment to supply chain management and customer service.
Smart Cities must transform from fragmented projects to integrated urban platforms
The Smart City Paradigm: A New Urban Model
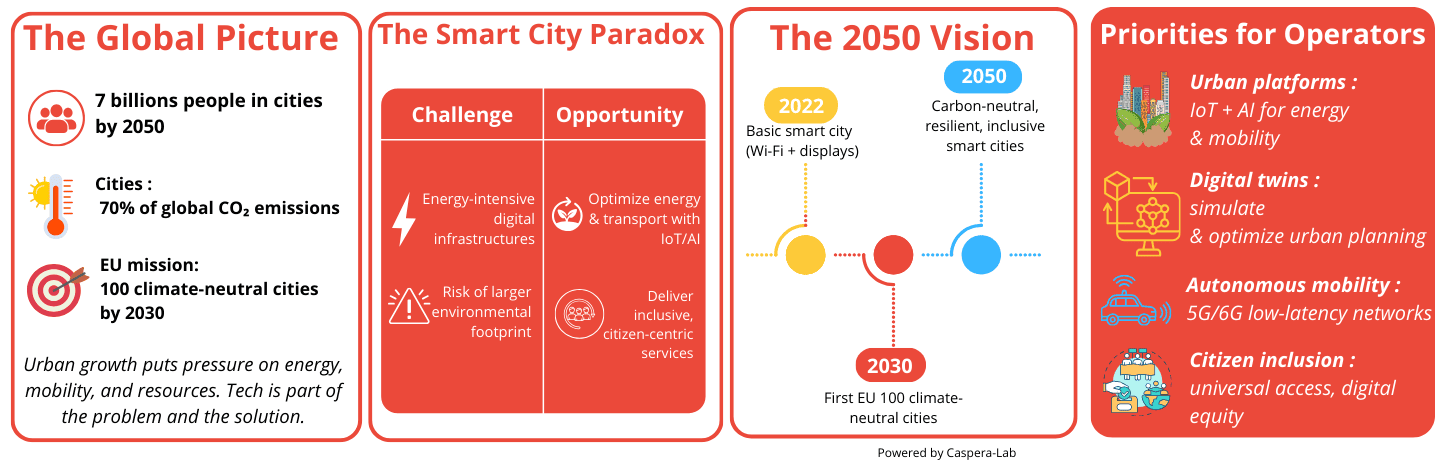
The concept of a "smart city" is often oversimplified, reduced to a municipality with ubiquitous Wi-Fi and advanced digital displays. An expert-level definition, however, reveals a far more complex and holistic urban model. A smart city is an urban center that strategically leverages technology, human capital, and sound governance to enhance sustainability, efficiency, and social inclusion for its inhabitants and businesses. It transcends the simple deployment of digital tools and instead focuses on their intelligent application to optimize resource utilization, reduce emissions, upgrade essential services, and foster a more responsive city administration. The European Union's Smart Cities Marketplace exemplifies this multi-faceted approach by acting as a collaborative forum that unites cities, industries, investors, and researchers with the shared objectives of improving citizens' quality of life and meeting European energy and climate targets.
The foundational premise of a smart city presents a critical paradox. While the model is heralded as a key solution to pressing urban challenges such as climate change and resource scarcity, its very existence is dependent on a massive, energy-intensive technology ecosystem. This creates a central tension that must be explored. The smart city is simultaneously a powerful driver of environmental solutions and a significant contributor to the global digital footprint. This report explores this duality, analyzing how the promises of smart cities can be reconciled with the realities of their environmental impact.
The 2050 Vision: A Blueprint for a Liveable Future
By 2050, the global urban population is projected to reach 7 billion people. The vision for a truly smart city is not merely about technological advancement but about creating urban environments that are sustainable, resilient, and inclusive. By 2050, smart cities are envisioned to be carbon-neutral, powered by large-scale renewable energy, and defined by circular economies and abundant green public spaces. The European Union has already set an ambitious mission for 100 cities to achieve climate neutrality by 2030 to serve as a catalyst for a broader transformation by 2050.
The future of smart cities will be defined by the convergence of the physical and digital realms. This includes the widespread adoption of digital twins to simulate and optimize urban planning, the rise of autonomous transportation, and the development of next-generation infrastructure that is inherently more sustainable and efficient. This requires a holistic approach that prioritizes not just efficiency but also resilience to climate change and social equity. The UN's Sustainable Development Goals for 2050 emphasize tackling urban poverty, ensuring universal access to basic services, and strengthening local governance to create cities that are inclusive and equitable for all residents.
Inspire
Our Inspire portfolio broadens strategic vision and equips decision-makers to navigate the challenges of the Beyond Telco era.
It offers two exclusive masterclasses designed to spark new perspectives and open actionable pathways:
For telecom and enterprise leaders: a deep dive into sustainability & energy efficiency, green IT, and next-generation datacenters. This masterclass shows how environmental responsibility is not just a compliance issue but a lever for competitiveness, innovation, and growth. For territorial leaders, mayors, and local decision-makers: a focus on smart cities — how IoT, AI, data, and digital platforms can be harnessed to create more efficient, inclusive, and sustainable urban ecosystems.
Together, these sessions challenge established mindsets, inspire leaders to rethink strategies, and reveal new growth models that deliver value for business, citizens, and the planet.
Assess
Our Assess portfolio equips leaders with a precise view of where they stand today and the priorities they should set for tomorrow. It is built on three advanced maturity frameworks:
Sustainability for telecom and enterprise leaders: measuring energy efficiency, green IT, and datacenter optimization to uncover practical ways to cut carbon impact while boosting operational performance.
Smart Cities for territorial leaders and policymakers: assessing governance, technology adoption, citizen engagement, and data-driven services to steer sustainable and inclusive urban development.
AI & Citizens for organizations and territories: evaluating how ready they are to embrace artificial intelligence responsibly, balancing innovation with ethics, privacy, and public trust.
Together, these assessments deliver a data-driven, comparative view that enables leaders to benchmark against peers, set clear priorities, and accelerate their transformation with confidence.








